Effective marketing is all about personalization. To target current and potential customers, you must know what they’re looking for so you can explain how your company will serve their needs.
Data is the best way to personalize your marketing efforts because it provides real information about your current and prospective customers that you can transform into actionable insights and tailored campaigns.
We recommend using a variety of data types—including zero-, first-, second-, and third-party data—to capture different elements of your customers’ personas and needs. In this guide, we’ll focus on first-party and third-party data and explain how you can leverage this information to target your audience:
- First-Party Data FAQs
- Second-Party Data FAQs
- Third-Party Data FAQs
- Zero-Party Data FAQs
- Zero vs. First vs. Second vs. Third-Party Data: Comparing Different Data Types
- How to Combine Different Data Types in Your Marketing Strategy

First-Party Data FAQs
What Is First-Party Data?
First-party data refers to the information that customers share through their interactions with your business’s owned properties, such as your website, app, or physical store. Since it originates from your direct relationship with users, first-party data is generally considered reliable and trustworthy.
What Are Some Examples of First-Party Data?
First-party data can include:
- Demographic information, such as age, gender, and location
- Communication preferences
- Contact information
- Social media engagement
- Website activity, including clicks, downloads, and searches
- Purchase history
- Preferences and behaviors
Imagine you own a moving company, and a customer visits your online store to purchase packing materials for their upcoming relocation. During this process, you may collect their contact information, and you’ll have a record of anything they buy after they check out. This is considered first-party data.
What Is the Value Proposition of First-Party Data?
The value of first-party data lies in its authenticity, relevance, and potential for improving business outcomes. Tapping into these direct audience insights enables:
- Informed decision-making. When users give consent to share their data, they are more likely to provide accurate and reliable information. This leads to higher-quality data that your business can use to make better decisions.
- Agility. With direct access to audience insights, you can identify emerging trends or shifts in preferences and quickly adjust your strategies. This agility will give your business a competitive edge.
- Enhanced customization. According to a study by Twilio, 78% of businesses consider first-party data their most valuable data source for personalization. Creating tailored marketing campaigns and retargeting strategies based on real user insights improves customer engagement.
- Long-term customer relationships. By nurturing relationships through personalized interactions, your business can establish long-lasting connections with customers, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Keep in mind that while collecting first-party data is essential, these benefits only emerge when you analyze, interpret, and act upon this information.
What First-Party Data Challenges Do Businesses Face?
While most marketers understand that first-party data is crucial for effectively reaching customers, tailoring their messaging, and building lasting customer relationships, many find it challenging to manage and leverage this information.
Here are some common issues businesses face regarding first-party data and how your company can resolve them.
Consolidating data into a single source of truth
From your website to social media to point of sale (POS) systems, first-party data comes from many different sources. Generally speaking, the more methods you use to collect first-party data, the more robust your understanding of your customers will be. However, using multiple data collection sources can also lead to fragmented, isolated pieces of information called data silos.
When your customer data is siloed in different systems, it’s difficult to take full advantage of this useful information, slowing down the decision-making process. Additionally, you may have duplicate or inconsistent data across systems, leading to delayed, misinformed decisions that waste resources on the wrong customers or prevent you from reaching the right ones.
For example, a customer may have recently updated their email address when making a purchase online. But if you still have their old email address stored in your marketing platform, you won’t be able to reach them with product updates and discounts.
To prevent siloed data, store your first-party data in one central system, like a CRM or CDP. That way, you can confidently and efficiently use this data to inform your decisions.
Maintaining customer data quality
Even with all of your data in one place, it can still become inaccurate fairly quickly. Between customers moving, graduating, switching jobs, or even just entering data incorrectly, their information can easily become outdated or incorrect.
That’s why it’s so important to invest in data hygiene. When you take the time to create data entry standards, cleanse your data, and validate it, you ensure your customer data is accurate and up-to-date. Then, you can develop well-informed customer segments based on characteristics like age, location, and income to target them more effectively.
Additionally, clean data helps you actually get in touch with your customers. For instance, if you continue sending direct mail to a customer’s old home address, you not only waste these resources on the wrong household but also miss spreading your message to the intended customer. Audit your CRM or CDP regularly so you can make updates as needed to keep your data accurate.
Balancing data usage with customer privacy
As more companies leverage customer data to improve their operations, there has been a greater focus on protecting customers’ privacy and giving them control over how companies use their personal information.
For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) protects the data privacy of European Union (EU) citizens by ensuring companies only collect necessary data, are transparent about why they’re collecting this data and how they’re using it, obtain consent for collecting and using customer data, and enable customers to access, correct, and delete their own data.
Even if your business operates outside the EU, GDPR applies if you have any customers living in the EU. Other data regulations you might have to follow include the Fair Information Practices Principles (FIPPs) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), among others.
As conversations about data privacy come to the forefront, customers have also expressed their concerns about how companies use their data; 80% of adults worldwide say they’re concerned about their privacy, and 69% say they’re more concerned now than ever before.
So, how can you continue to use first-party data to strengthen your marketing efforts while also respecting customers’ wishes and following data privacy regulations? We recommend taking the following steps:
- Determine which regulations apply to your business. Start by researching the rules and regulations your company must follow. The U.S. State Privacy Legislation Tracker is a helpful resource from the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP), highlighting relevant laws applicable to each state. Since these regulations are constantly changing, you must stay diligent to ensure you remain compliant.
- Be transparent about data collection and usage. Some customers may not mind if you use their data, but they expect you to be transparent about it. Always obtain consent, inform them that you’re collecting their data, and explain what you’re using their information for.
- Store data securely. The system you use to store your data should help protect your customers’ sensitive and personal information. Choose a database that offers features like data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and SOC 2 Type II compliance to keep customer data safe.
Maintaining proper data hygiene will also help protect customer data privacy. Customers may change their minds about whether and how they’d like you to use their data, so regularly auditing your database can ensure your customer data preferences are up to date. Additionally, you can use data suppression services to identify customers who have registered with the ANA’s DMAChoice™ Program (a Do Not Mail service) and avoid contacting them via direct mail.

How Can Marketers Leverage First-Party Data?
Conduct a data quality assessment.
A data quality assessment ensures the information your business uses for analysis, targeting, and personalization is accurate and up-to-date.
To begin, conduct a thorough audit of your collected data and make a note of any anomalies or errors. Then, employ the following data hygiene best practices:
- Standardize data entry. Establish guidelines for data entry and implement automated checks to validate data entered against these standards. For instance, in a point of sale system (POS), you could ensure that all currency symbols are formatted using “USD” to reduce confusion when analyzing transaction data.
- Cleanse data. Use data cleansing tools (or data hygiene providers like Deep Sync!) to remove duplicated data, correct inaccurate entries, and handle missing values. That way, if a customer accidentally submits their email address without the “@” symbol, you can rectify the issue and be confident that you’re reaching out to a real address.
- Validate data. Verify the accuracy of your data against a third-party data provider like Deep Sync. Because your customers’ lives and preferences are constantly changing, routine updates are necessary so you can continue to engage with them. In fact, the rate of data decay on a consumer dataset is 25-30% per year.
Data hygiene is an ongoing process, meaning you’ll need to regularly monitor your first-party data for duplicates, inconsistencies, and errors. While this may seem overwhelming, it will ultimately lead to more effective decision-making. Consider a partner like Deep Sync for your routine data hygiene needs.
Segment customers.
Segmentation refers to the process of dividing customers into distinct groups based on insights gleaned from customer data. A key component of audience targeting, it’s crucial for delivering better, more personalized experiences to customers.
With well-defined segments, you can tailor outreach to specific groups within your target audience and deliver content that resonates with their unique interests, preferences, and behaviors. For example, a clothing retailer may choose to segment customers according to demographic data, such as age, gender, location, income, and occupation. Then, they may target young, fashion-forward customers with trendy designs and advertise classic styles to an older, more conservative segment.
To uncover your ideal customer segments, use an automated profiling service like Deep Sync One’s Customer Insights. Simply upload your first-party data to compare it against Deep Sync’s national consumer database. In a matter of minutes, you will receive an actionable report that ranks the demographic elements in your customer file based on our findings and audience recommendations that you can apply to future campaigns.
Use predictive analytics.
In addition to using first-party data to personalize outreach, you can use it to predict future outcomes. Predictive analytics applies statistical algorithms to historical data to forecast customer behavior and improve campaign performance metrics, such as:
- Churn. Analyze engagement metrics or customer feedback to identify customers who are at risk of churning (i.e., discontinuing their relationship with your brand), and send them materials that incentivize their ongoing support.
- Cross-selling and upselling. Use a customer’s purchase history to recommend relevant additional products or upgrades to drive revenue growth.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). Review past purchase behavior and engagement history to predict the future value of individual customers. These insights will help you decide which customers to prioritize for retention and upselling strategies.
- Revenue. Use historical sales data to identify seasonal trends, evaluate the impact of marketing initiatives on revenue, and allocate your resources more effectively.
To generate this information, you can use several different types of predictive models, including regression analysis, decision trees, clone models, and combination models. Before getting started, ensure your model aligns with your specific marketing goals.
Optimize campaigns and experiences.
Once you’ve cleaned, organized, and analyzed your first-party data, you can apply it toward optimizing customer experiences via:
- Omnichannel marketing. Customize the timing of communications based on user behaviors and preferences, ensuring messages reach users on their preferred channels when they’re most likely to engage.
- Retargeting. Deliver retargeting ads that display the exact products users viewed or abandoned in their online shopping carts, encouraging them to return and complete the purchase.
- Lead generation. Customize lead magnets, landing pages, and calls to action to address each customer’s specific pain points or interests.
By effectively harnessing first-party data in these ways, you can increase engagement, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive better results for your business.
Second-Party Data FAQs
What Is Second-Party Data?
Second-party data is another organization’s first-party data that they share with your business.
It enables you to learn more about current or potential audiences without spending the time and resources to collect this information yourself, making second-party data extremely cost-effective.
What Are Some Examples of Second-Party Data?
Let’s say a hotel shares data about customer stay frequency and booking history with a car rental service. The car rental company could use this second-party data to share ads and discounts with customers who stay at the hotel often.
How Do You Collect Second-Party Data?
You may partner with other companies to exchange data or purchase information through a data marketplace. Like first-party data, second-party data is usually reliable because it comes directly from customers. Just verify that the partner sharing this information complies with relevant data privacy regulations.
Third-Party Data FAQs
What Is Third-Party Data?
Third-party data (also called 3rd party data, 3p data, or 3pd) is information that external sources or data providers collect and package.
This data does not come directly from the consumers it’s attached to. Instead, providers acquire this information from various sources and compile it to create datasets that businesses can leverage. Then, companies append this third-party data to round out their databases and reach new audiences.
What Are Some Examples of Third-Party Data?
Data providers typically offer a wide array of data to satisfy various business needs. This information may include:
- Contact information
- Demographics
- Education
- Marital status
- Home ownership and property data
- Presence of children in the home
- Income
- Net worth
- Lifestyle information
With an estimated 182 zettabytes of data to be created, captured, copied, and consumed worldwide in 2025, there is an overwhelming amount of information available. Brands can leverage this information to transform their marketing approaches and effectively reach target audiences. Data providers do the heavy lifting of sourcing, organizing, and packaging this information to make it digestible and actionable for companies.
What Are The Benefits of Third-Party Data?
When you leverage third-party data, your team receives the following benefits:
- Greater efficiency. Third-party data requires little time and effort to acquire. All you have to do is contact a data provider. Plus, 3rd party data companies often package data in a way that eliminates the need for additional organization and categorization, saving your team even more time.
- Enriched customer profiles. Third-party data enables you to learn valuable insights about your customers that you may not be able to obtain through traditional interactions. You can then use this data about their habits, behaviors, and demographics to personalize your audience targeting.
- Broadened reach. While third-party data helps you learn about your current customers, it can also enable you to identify lookalike audiences composed of consumers who resemble your customer base. You can then target these potential customers and expand your reach to additional people who may engage with your brand.
- Easier scalability. Data providers can grant your business access to extensive datasets, enabling you to expand your customer base quickly. This information can also help you tap into new markets and scale up. For example, if you typically sell to adults but want to start targeting a younger audience, you can use a youth marketing dataset to jumpstart your efforts.
- Competitive edge. The more data you have, the more you’ll understand your customers and industry. Third-party data provides businesses a unique advantage because they can transform this information into actionable insights and hop on consumer trends before they become apparent to other companies.
Third-party data is integral to successful marketing campaigns, with about 61% of digital marketers using this type of data. While you must take extra care to ensure third-party data is accurate and collected in alignment with relevant data privacy regulations, it digs deeper into customer insights you may not be able to glean from typical interactions with your audience, enabling you to enrich your database and personalize your campaigns even further.

How Do You Collect Third-Party Data?
To acquire third-party data, companies must work with a data provider. Data providers compile data from a variety of sources, such as:
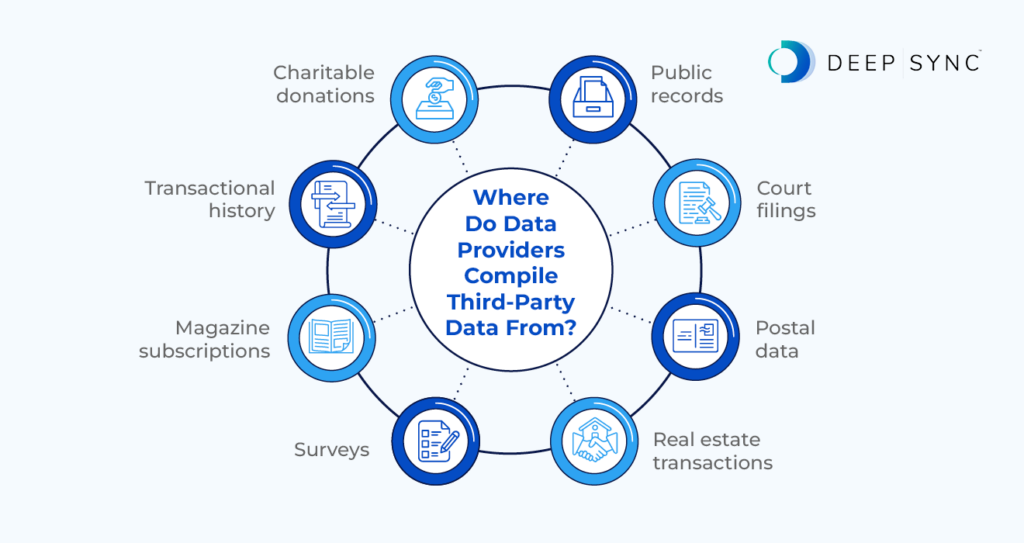
- Public records
- Court filings
- Postal data
- Real estate transactions
- Surveys
- Magazine subscriptions
- Transactional history
- Charitable donations
Many companies license third-party data through a list provider, DSP, data management platform (DMP), or data marketplace. Since you don’t always have insight into where third-party data comes from, you must research your third-party data provider to ensure they use reliable sources and follow all data privacy regulations.
How Should Marketers Choose a Third-Party Data Provider?
Like with any critical business decision, conducting research is crucial when selecting a third-party data provider. Compare companies’ offerings and pricing options to determine which best suit your organization’s preferences, budget, and goals.
While different providers may cater to specific niches and specialties, in general, you should look for a 3rd party data provider that:
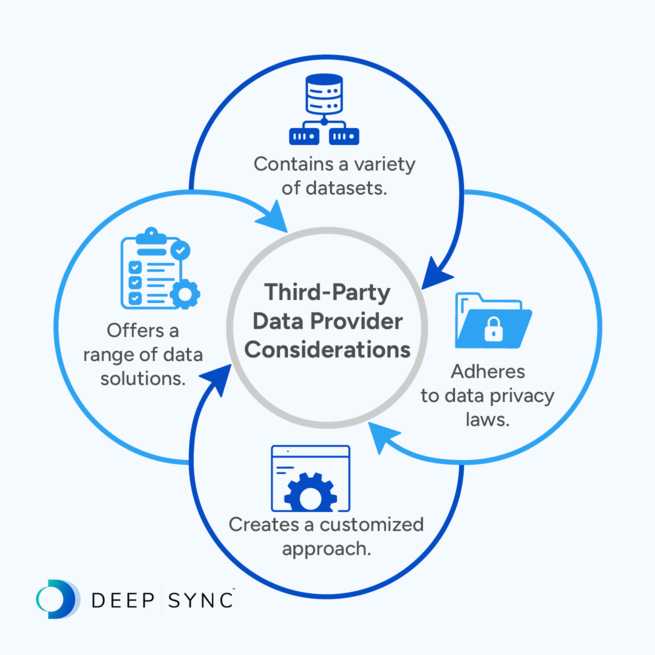
- Contains a variety of datasets. The best data providers package data for many different purposes and businesses. Their expertise and resources enable them to help any brand with its data needs and propel it in front of its target audiences. Additionally, choosing a data provider with various data types will ensure you can stick to one provider for multiple campaigns instead of continuously searching for new data sources.
- Adheres to data privacy laws. Data experts know security is a top priority for building trust between brands and customers. The right data provider will collect all data legally, follow applicable privacy and compliance guidelines, and note any data security certifications they hold.
- Creates a customized approach. Look for a data provider willing to take the time to discuss your data goals and how they can help you achieve them using third-party data. Working with a data provider should be a partnership in which your company explains its needs and preferences, and the provider develops a customized approach based on your input.
- Offers a range of data solutions. While sourcing and appending third-party data can improve your marketing efforts, providers can support your data goals in many other ways. When you find a data provider that offers various data solutions—from data quality reports to identity resolution—you can work with them for the long term to completely transform your data-driven marketing approach.
When you find a data provider that fits your brand’s needs, bring your team together to make the final decision. Getting different perspectives on the provider’s approach and offerings will ensure you choose the right provider for your company.
Zero-Party Data FAQs
What Is Zero-Party Data?
Zero-party data is information customers voluntarily share with your business. Businesses can use customers’ honest feedback to improve operations and personalize their marketing campaigns to reflect customer preferences.
What Are Some Examples of Zero-Party Data?
When a customer fills out a feedback form or poll, that information is zero-party data.
How Do You Collect Zero-Party Data?
You can collect zero-party data from surveys, preference centers, or in-person interactions.
Zero vs. First vs. Second vs. Third-Party Data: Comparing Different Data Types
Now that you’re familiar with different data sources, let’s review their differences:
| Zero-Party Data | First-Party Data | Second-Party Data | Third-Party Data | |
| Source | Customers | Customer interactions with owned properties | Partnership or data marketplace | Data provider, demand-side platform (DSP), data management platform (DMP), or data marketplace |
| Collection Method | Surveys, preference centers, personal interactions | Website, app, physical store, other owned properties | Website, app, physical stores, other owned properties | Aggregated from various sources |
| Collected with Consent | Yes | Yes | Must verify with provider | Must verify with provider |
| Accuracy | High | High | High | Depends on provider |
| Potential Use Cases | Improving customer experiences based on feedback | Creating tailored marketing campaigns based on customer data and insights | Gaining a deeper understanding of current customers to better target them | Scaling your marketing efforts to broaden your reach |
| Examples* | Interests, product feedback | Demographics, contact information | Purchase activity, loyalty program data | Income, home ownership data |
*Note that the same data types can fall under multiple categories depending on how they’re collected. For example, demographic information is considered first-party data if a customer enters it when using your website, as well as third-party data if purchased from an external source. Additionally, purchase history is first-party data if it pertains to your business’s products or services, and second-party if it concerns purchases from a different company.
How to Combine Different Data Types in Your Marketing Strategy
Each data type offers its own unique benefits to your marketing strategy. While first-party data keeps your strategy strong amid third-party cookie instability, third-party data provides unparalleled opportunities to understand and reach your target audience.
By combining different data types, you’ll build a holistic marketing strategy that maximizes your return on investment (ROI). Follow these steps to incorporate various data types into your approach:
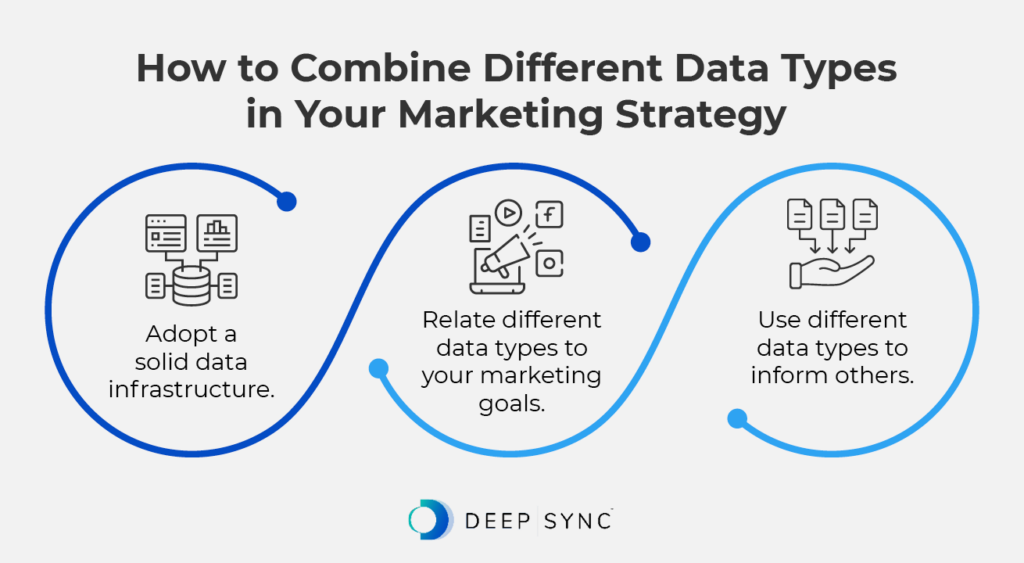
- Adopt a solid data infrastructure. In addition to your CRM, leverage a CDP to unify different data types. This platform gathers information from various sources and transforms that data into customer profiles. That way, you can avoid data silos and get a better understanding of your customers by analyzing different data types.
- Relate different data types to your marketing goals. Determine which types of data would be most useful for different marketing objectives. For example, if you’re looking to personalize messages to your current customers’ needs, you may leverage zero-party and first-party data, whereas if you’re trying to reach new audiences, you may rely more heavily on second-party and third-party data.
- Use different data types to inform others. You can use the data you have from one source to confirm or improve data from another source. Let’s say you collect third-party data about customer lifestyle preferences. To confirm this information, you may survey your customers, collecting zero-party data that speaks directly to your audience’s interests.
The key to successfully using different data types is keeping your customer data up to date. Regularly audit your data for accuracy and invest in data hygiene measures to keep it clean.
Wrapping Up
Working with a trusted data provider like Deep Sync enables your company to maximize the value of your first-party data, access a variety of unique third-party datasets, dig deep into customer insights, and supercharge your marketing efforts. To get started with your custom data marketing approach, contact us today.
If you want to learn more about using data to fuel your marketing campaigns, check out these additional resources:
- What Is Marketing Data? How to Leverage These Insights. Get a more general overview of marketing data, the different types, and how you can use it for more targeted campaigns.
- What Is Data Enrichment? How To Unlock Marketing Insights. Explore how you can enrich your database with third-party data following best practices.
- What Is Identity Resolution? The Ultimate Marketer’s Guide. Dive deep into the identity resolution process, which unites disparate customer data into unified profiles.















0 Comments