In a crowded marketing landscape, you must stand out from the competition. It’s no longer enough to have the best product or service on the market; you must also reach the right customers at the right time through the right channels with innovative messaging.
Understanding your audience is the key to marketing success. When informed by your audience’s preferences and interests, you can tailor your outreach to them, boosting your marketing return on investment (ROI) and creating a better experience that resonates with customers. That’s where marketing data comes into play.
In this guide, we’ll explore marketing data and how to apply it. We’ll cover:
- What is marketing data?
- What are the benefits of using marketing data?
- Where can you source marketing data from?
- What is data-driven marketing?
- 4 Steps to Implement Marketing Data into Your Strategy
With the help of relevant marketing data, you’ll create campaigns that grab people’s attention, speak directly to their needs, and persuade them to make a purchase. Let’s get started by answering some common marketing data questions.

What is marketing data?
Marketing data is any information used to power marketing efforts. This data helps businesses better understand their customers and create campaigns that resonate with them.
The main types of marketing data include:
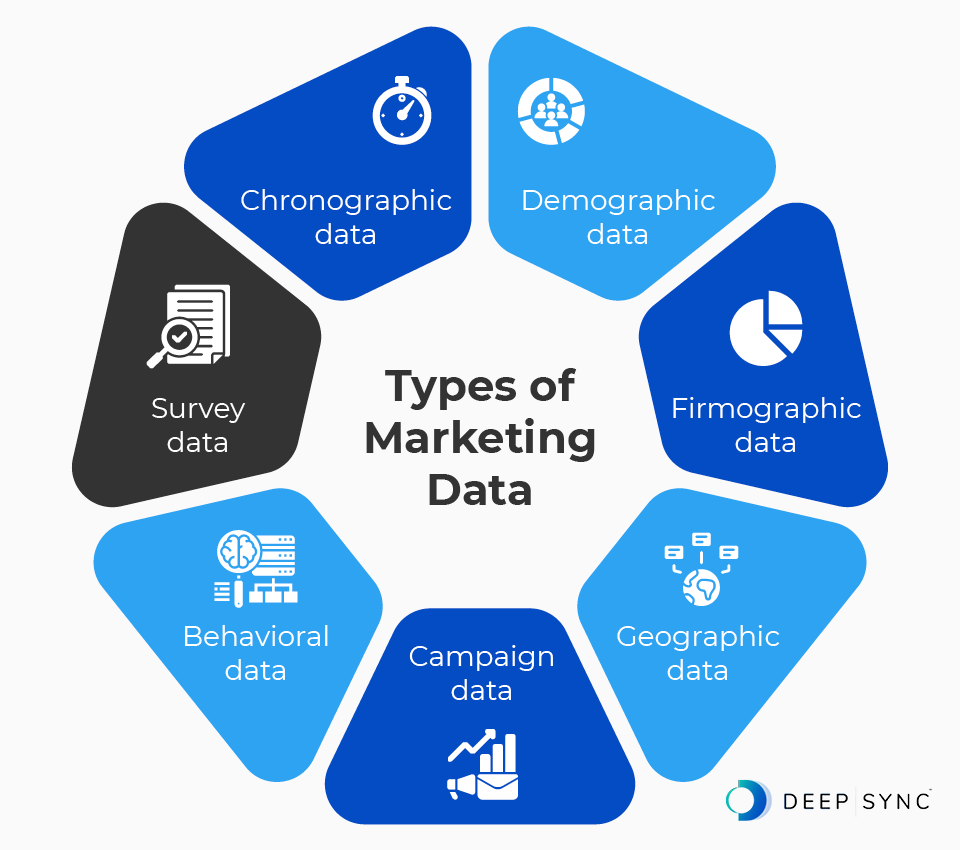
Demographic data
Demographic data refers to information that tells you more about who your customers are as people. This type of marketing data includes elements like:
- Age
- Gender
- Income
- Net worth
- Marital status
- Level of education
- Presence of children in home
- Lifestyle attributes (hobbies/interests, student status, occupation)
This information empowers you to make customized product or service recommendations and tailor your offerings and campaigns to customers’ needs. For example, knowing your average customer’s income can help you price your offerings appropriately, understanding the age breakdown of your customers can help you leverage the marketing channels they’re most likely to use, and determining which customers have children can help you narrow your outreach for back-to-school campaigns on those households.
Firmographic data
Companies with business-to-business (B2B) offerings may focus more heavily on firmographic data, which is information about businesses instead of individuals. This type of marketing data includes:
- Company name
- Industry
- NAICS code
- Internal structure
- Annual revenue
- Size
- Market segment
- Location
- Phone number(s)
- Website address
- Email addresses
- Key contacts
Like demographic data, firmographic information can help you personalize your outreach to different business needs and pain points. For instance, a software provider may emphasize its small business plan to companies with under 500 employees or offer a discount on one of their larger plans.
Geographic data
Knowing your customers’ latitude and longitude coordinates allows you to narrow your focus even further and hyper-target your audience.
For example, a grocery store chain that knows where its customers are located can send deals and news specific to the store each customer is closest to. Regarding B2B marketing, a consulting firm may highlight its ability to perform hands-on, in-person services to businesses within a certain radius.
Campaign data
Your past campaign data should fuel your future marketing efforts. These quantitative metrics can help you determine which strategies and channels are most effective so you can replicate successful elements and rework low-performing ones.
This marketing data includes key performance indicators (KPIs) like:
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Conversion rate
- Cost per acquisition (CPA)
- Cost-per-click (CPC)
- Email open rate
- Return on investment (ROI)
Make sure you have a system to track these metrics and store them in your customer relationship management platform (CRM) so you can refer back to them.
Behavioral data
The way customers interact with your brand is behavioral data. This information helps you understand each customer’s individual relationship with your business and tailor your communications accordingly.
This type of marketing data includes:
- Website visits
- Website clicks
- Purchase history
- Email engagement
Let’s say your company sells vitamins in packages that last three months. Using behavioral marketing data, you can identify which customers will likely run out of vitamins soon and email them asking if they’d like to repurchase.
Survey data
Collecting feedback lets you hear directly from your customers and adjust your marketing strategy to align with their preferences and expectations. This qualitative data can supplement your collected quantitative information and add more context to customers’ behavior.
Regularly ask customers for their feedback on your products, services, marketing efforts, or overall experience with your business so you can constantly improve your offerings and outreach strategy.
Chronographic data
Chronographic data refers to current events or trends that could impact sales and customers’ likelihood of buying. This type of marketing data includes:
- Holidays or special occasions
- Company mergers
- Company acquisitions
- Company recruitment drives
For example, a retailer may ramp up its marketing efforts in the fall in preparation for the holiday season, and a consulting firm that knows a prospect has just received more funding through an acquisition may reach out to finalize a deal.
What are the benefits of using marketing data?
Collecting marketing data empowers you to get to know your customers on multiple levels. This deeper understanding of your audience allows your company to:
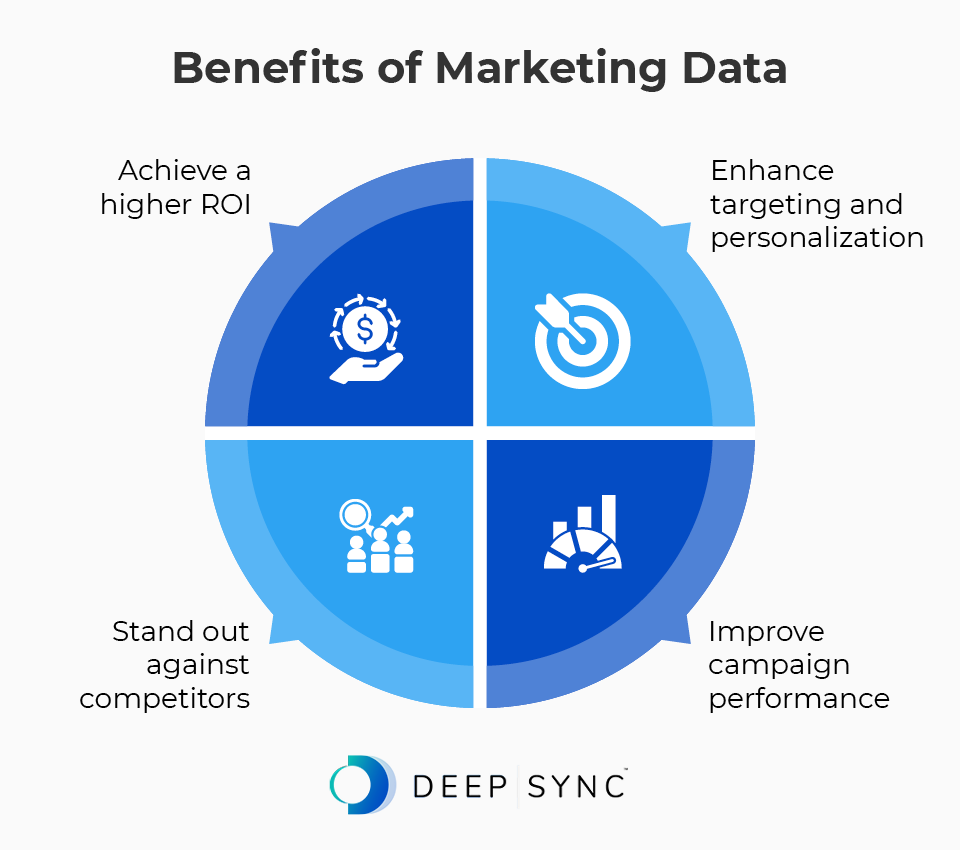
- Enhance targeting and personalization. Gathering and analyzing vast amounts of customer marketing data—such as demographics, preferences, behavior patterns, and purchase history—helps guide segmentation and enables marketers to create more personalized campaigns. This targeted approach helps engage customers, build stronger relationships, and drive higher conversion rates.
- Improve campaign performance. Data-driven marketing empowers marketers to continuously monitor, measure, and optimize campaign performance. By tracking performance metrics in real time, marketers can quickly identify underperforming campaigns or channels and make data-informed adjustments to improve results.
- Stand out against competitors. With accurate marketing data, you can stay up-to-date with market trends and make more informed business decisions. Additionally, customers will appreciate your efforts to personalize your communications to their needs, allowing you to shine amongst other industry players.
- Achieve a higher ROI. Businesses that use data marketing strategies drive five to eight times as much ROI as businesses that don’t. Leveraging marketing data allows businesses to optimize campaigns and allocate resources more effectively, increasing efficiency and cost savings.
Overall, marketing data creates a more fulfilling, individualized customer experience that can boost sales and help retain customers over the long term.

Where can you source marketing data from?
Marketing data can come from a variety of sources. Typically, marketers use the following labels to indicate where they’ve obtained their data from:
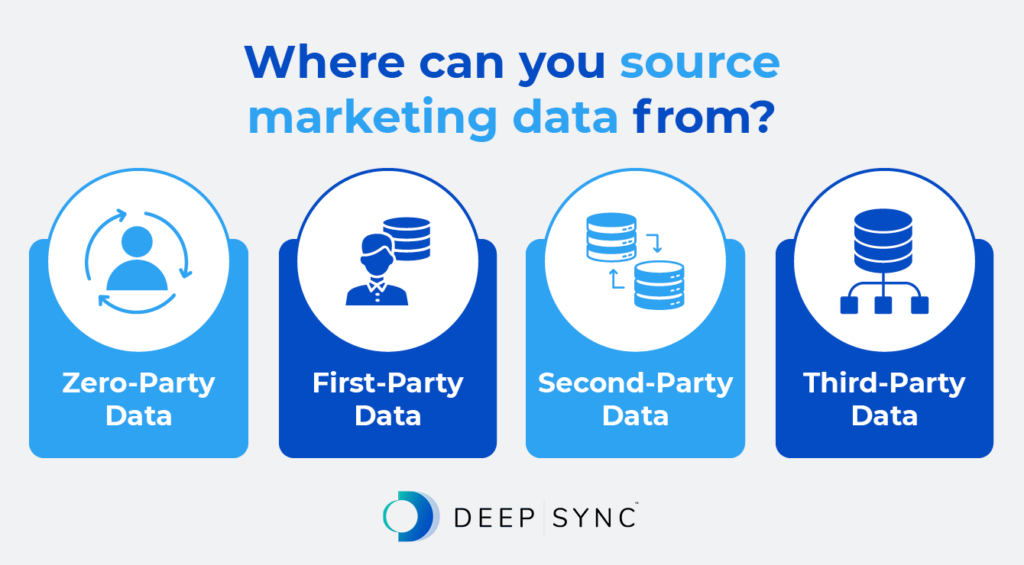
- Zero-party data: This is marketing data that your customers voluntarily share through surveys, preference centers, and in-person interactions. Encourage customers to share their honest feedback so you can align your marketing campaigns with their true preferences.
- First-party data: This category includes information your customers share with your organization when they interact with your website, app, physical store, or other owned properties. Typically, first-party data includes demographic and behavioral information. Since customers give this information to your organization directly, you can trust that it’s accurate and use it to enhance your outreach.
- Second-party data: This form of marketing data is another organization’s first-party data that they share with your business through a collaboration or partnership. It can often help you gain a deeper understanding of your current customers and expand your reach.
- Third-party data: This category includes information from an external provider. Third-party data can supplement your first-party data and provide information you may not have the resources to collect on your own. As a result, you can improve your targeting and even reach a broader audience.
Combining these marketing data types can provide a holistic understanding of your customer base and help create more impactful campaigns.
What is data-driven marketing?
Put simply, data-driven marketing is the practice of basing your brand’s marketing and communications strategies on the data you’ve gathered about your target audience.
Combining the marketing data your brand collects and information from third-party sources gives you the insights you need to optimize your campaigns and reach your target audience.
How is data marketing different from traditional marketing approaches?
While traditional marketing practices are based on long-held assumptions or gut feelings, data marketing is based on quantifiable facts from your customer data. What once would have been a mass, untargeted marketing campaign based on an educated guess is now a specific, factual effort based on accurate marketing data.
What are the challenges of data-driven marketing?
Companies new to data marketing may face challenges when launching their first campaigns. These may include:
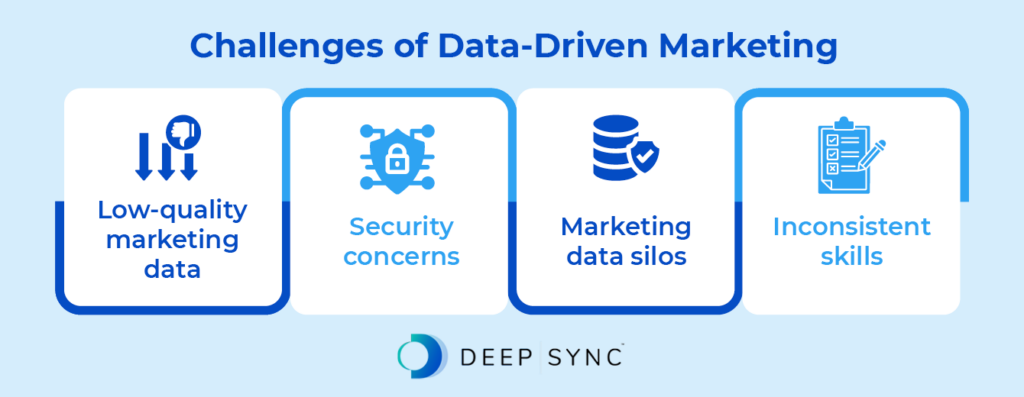
- Low-quality marketing data: Inaccurate, incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent marketing data can lead to costly mistakes, such as targeting the wrong audience. To ensure your data is high quality and will help achieve your marketing goals, regularly audit your database and standardize the collection process.
- Security concerns: Large databases risk being breached by unauthorized users. Implement security measures like data encryption, firewalls, and limited access rights. Use reputable data sources and implement a comprehensive data breach response plan in case of an emergency.
- Marketing data silos: Siloed data refers to data stored in a standalone system that doesn’t sync with other relevant information. This makes it difficult to share information across departments and can hinder collaboration. To prevent this issue, centralize marketing data storage and use data management tools that facilitate data sharing across teams.
- Inconsistent skills: Some team members may have a better understanding of data collection and analysis than others. Invest in ongoing training to ensure that everyone on your marketing team is equipped with the latest tools and techniques to facilitate data marketing.
While these may seem like large institutional hurdles to overcome, a strong data marketing strategy is still within reach for your company. Consider partnering with a team of data experts like Deep Sync to prevent these problems from arising and set your campaigns on a path to success.

4 Steps to Implement Marketing Data into Your Strategy
With a better understanding of the importance of marketing data, you’re ready to incorporate it into your strategy via the following steps:
1. Set clear goals.
Goal-setting should be the first step of any data-driven marketing campaign. Specific and measurable marketing goals help teams stay on track and make informed decisions about how best to optimize their campaigns. By focusing on key objectives, you can also allocate resources more effectively.
A few data marketing goals could be:
- Growing your Millennial audience.
- Successfully introducing a new vertical.
- Exploring social network marketing for the first time.
- Holding an event series in a specific geographic location.
Data can directly improve each of these efforts. For example, marketing data can reveal how Millennials are already interacting with your brand, allowing you to optimize those channels. It can also guide location-based targeting, helping drive foot traffic to your event.
2. Collect data to inform decision-making.
Consider which information will inform your strategy and help you achieve your goals. Then, decide how you will access that marketing data, whether through:
- In-house data collection: In-house data refers to the data that a company collects and maintains on its own customers and operations. Whether collected through social media engagement, email list sign-ups, or transactions, this information is valuable for understanding how customers interact with your brand.
- Third-party data collection: Conducting a third-party data append fills in the gaps about your target audience and provides insight into their interests outside your business. For example, are they homeowners? Are they interested in environmental causes? Use this additional data to create more personalized and targeted marketing campaigns.
Once you’ve collected your marketing data, it’s time to process it to ensure it’s useful. Data hygiene is the practice of ensuring the accuracy of the information you collect. It involves fixing incomplete, incorrect, and duplicate entries so that there is one complete and accurate entry for each data point in your system. The process begins with conducting an audit of your database and addressing key issues.
For instance, let’s say your marketing list has multiple email addresses or phone numbers for the same individual, potentially leading you to send marketing messages to the same person multiple times. As a result, you’ll waste resources and provide a negative customer experience. By using data hygiene practices to identify and rectify duplicate records, your team can improve the accuracy and effectiveness of its campaigns.

3. Analyze and apply your marketing data.
With a complete and clean database, you can begin analyzing this information. Use your data marketing objectives to guide your team through the following steps:
- Determine which demographics or common characteristics will best address your objective. For instance, you may focus on factors like geographic location, age, buying history, communication preferences, or social network use.
- Segment your data by those characteristics. Group your customers accordingly to narrow your target audience. For instance, if you’re hoping to target Millennials, you’ll probably want to connect with them on their mobile devices, as the average Millennial spends about 4 hours and 36 minutes on a smartphone per day. Segment contacts by age and prioritize mobile-first marketing among this demographic.
- Put the insights unveiled by those groupings into action. You can apply your data analysis in various ways, including ad retargeting, dynamic advertising, paid search results, and even email and direct mail personalization.
Consider using A/B testing to produce the best possible marketing campaigns. A/B testing involves creating two slightly different campaign versions and measuring which version receives the most engagement. For instance, you might test different subject lines, call-to-action buttons, or images in an email campaign. You can then determine which approach is more effective and optimize the campaign accordingly.
4. Measure campaign performance.
Effective data marketing doesn’t end when your campaign does. The entire point of these strategies is to learn from the data and improve your marketing efforts.
Begin by monitoring and measuring the following marketing data metrics:
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads who take the desired action, such as making a purchase or submitting a form.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): The amount spent on creating a campaign to acquire a new customer.
- Engagement Rate: The level of interaction or engagement that users have with the campaign, such as likes, shares, or comments.
You should also pay close attention to who responded to your campaign. Were there any surprises, such as likely respondents ignoring the effort or unlikely respondents doing the opposite? Dig deeper to examine why they responded (or didn’t respond). Do your non-responders or non-buyers share any common characteristics that correlate with their response behavior?
Use this information to inform your future marketing efforts. With this analysis, you can identify buyer personas and expand your campaign prospects going forward.
Next Steps: Get Started with Marketing Data
Marketing data is the bedrock of modern marketing success. It empowers marketers to make well-informed decisions, target the right audience, and optimize campaign performance.
By applying the principles outlined in this guide and reaching out to our team of experts, you can unlock the full potential of your marketing data and stay ahead of the competition in today’s ever-changing landscape.
For more information on marketing data best practices, check out these additional resources:
- What Is Third-Party Data? The Ultimate Guide for Businesses. Learn how you can supercharge your marketing strategy with third-party marketing data.
- What Is Data Enrichment? How To Unlock Marketing Insights. Enhance your database to unlock more information about your customers and provide focus to your marketing strategy.
- What Is a Data Append? How to Improve Marketing Engagement. Conduct a data append to fill information gaps, develop more precise customer segments, conduct new forms of outreach, and narrow your target audience.













0 Comments